WATERFALL MODEL / LINEAR-SEQUENTIAL MODEL
- The Waterfall Model was first Process Model to be introduced. It is also referred to as a linear-sequential life cycle model because it illustrates the software development process in a linear sequential flow.
- In a waterfall model, each phase must be completed before the next phase can begin and there is no overlapping in the phases.
- Waterfall model is the earliest SDLC approach that was used for software development. It is very simple to understand and use.
- In "The Waterfall" approach, the whole process of software development is divided into separate phases. In Waterfall model, the outcome of one phase acts as the input for the next phase sequentially.
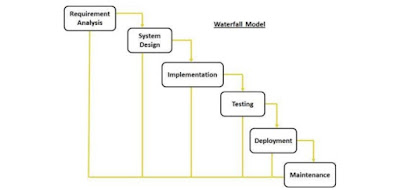
- Following is a diagrammatic representation of different phases of waterfall model.
- The sequential phases in Waterfall model are:
- Requirement Gathering and analysis: All possible requirements of the system to be
- developed are captured in this phase and documented in requirement specification
- documentation.
- System Design: The first phases are studied in this phase and system design is prepared.
- System Design helps in specifying hardware and system requirements and also helps in
- defining overall system architecture.
- Implementation: With inputs from system design, the system is first developed in small
- programs called units, which are integrated in the next phase.
- Each unit is developed and tested for its functionality, which is referred to as Unit
- Testing.
- Integration and Testing: All the units developed in the implementation phase are
- integrated into a system after testing of each unit.
- Post (After) integration the entire system is tested for any faults and failures.
- Deployment of system: Once the functional and non-functional testing is done, the
- product is deployed in the customer environment or released into the market.
- Maintenance: There are some issues, which come up in the client environment.
- To fix those issues maintenance is done. Also to enhance the product some better
- versions are released. Maintenance is done to deliver these changes in the customer
- environment.
- When to use waterfall model
- • Requirements are very well documented, clear and fixed.
- • Product definition is stable (no change).
- • Technology is understood and is not dynamic.
- • There are no ambiguous requirements (no double meaning and confusion).
- • Ample resources with required expertise are available to support the product.
- • The project is short.
- Advantages
- • Simple and easy to understand and use.
- • Easy to manage due to the rigidity (strictness) of the model. Each phase has specific
- deliverables (output) and a review process.
- • Phases are processed and completed one at a time.
- • Works well for smaller projects where requirements are very well understood.
- • Clearly defined stages.
- • Well-understood milestones (objective or target).
- • Easy to arrange tasks.
- • Process and results are well document
- Disadvantages
- • No working software is produced until late during the life cycle.
- • High amounts of risk and uncertainty.
- • Not a good model for complex and ongoing projects.
- • It is difficult to measure progress within stages.
- • Cannot accommodate changing requirements.
- • Adjusting scope during the life cycle can end a project.
Post a Comment
If you have any doubts, Please let me know
Thanks!